In the simplest, most basic form, the hematoma is just a bruise. In fact, the prefix "hema" means blood. A hematoma can occur when a blood vessel ruptures. Blood vessel rupture causes blood to ooze out and accumulate on the surface of the skin. When you see black and blue marks on your skin, you may be looking at the collected blood.
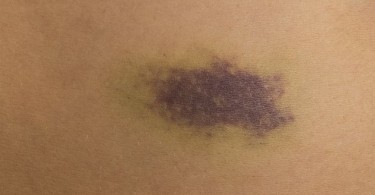
 Superficial hematoma or bruises are usually harmless. (Source: sawaddee3002 / iStock / Getty Images)
Superficial hematoma or bruises are usually harmless. (Source: sawaddee3002 / iStock / Getty Images) A Bruise Marks The Spot
When a blood vessel ruptures or tears, blood leaks out and forms a hematoma - localization Blood collection. Superficial bruises are the most common form of hematoma. When you hit a piece of furniture or something hits you, the wound can damage tiny blood vessels on your skin. The subsequent infiltration of bl into the skin can cause a surface hematoma - also known as a contusion or just a black and blue marker. The size of the bruise depends mainly on the area and strength of the impact.
Ice may help
The media is filled with images of people taking steaks with dark circles. In fact, there is some scientific basis behind this dramatic description - using cold compresses, not necessarily steaks. Immediate application of cold compresses to surfaces that are injured may limit the size and extent of developmental bruises. Low temperatures cause vasoconstriction in this area, which helps to prevent skin bleeding more quickly. You need to apply a cold compress as soon as possible to have a black-and-blue mark that has a big impact on development. Even if you miss a window that limits bruises, cold packs can help limit pain by eliminating nerves in the area.
Beware of other symptoms
Daily bruises are usually harmless and gradually disappear as your body sweeps through the leaked blood through a series of colors. However, bruises caused by fast-rising high-energy shocks may indicate more serious injuries. For example, there may be potential fractures or muscle damage. These more serious injuries can cause rapid swelling and may impede blood supply to the injured area. This complication - acute septal syndrome - requires immediate medical attention. If you are hit hard, the signs and symptoms you are looking for include: - Rapid expansion of the deformation of the area - Distorted shape of the injured area - Unable to move the affected area properly- Extreme or worse pain - numbness or tingling
Unexplained bruises need attention
Everyone has had an experience of noticing the bruises and not remembering how it happened. Occasionally this is normal. However, if you find frequent or multiple bruises without obvious explanation, it is best to arrange a visit to the doctor. Unexplained bruising can be due to the simple use of over-the-counter painkillers such as aspirin or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin). But in some cases, prone to bruising may indicate more serious conditions, such as bleeding disorders, leukemia or other forms of cancer. Although there is no need to panic for unexplained bruises, this is not something you should ignore.
Hematoma that you can't see is the most dangerous
Superficial hematomas are more common, but internal hematomas also occur, usually more severe. For example, a hematoma in or around the brain can be life threatening. These bleedings are usually due to falls, injuries or accidents - although traumatic events may initially appear to be relatively small. However, as the hematoma grows, it puts pressure on the brain. This pressure is usually exacerbated by brain swelling associated with injury. If not relieved quickly, stress on the brain can cause dangerous effects and may even lead to death. Signs and symptoms that require attention may indicate hematoma in or around the brain including: - increased headache - nausea and vomiting - abnormal sleepiness - confusion, mental retardation or slurred speech - sudden numbness, stinging or inability to move part of the body
Commentator: Tina M. St. John, MD.